How Much Do Teachers Make in Texas in 2023?

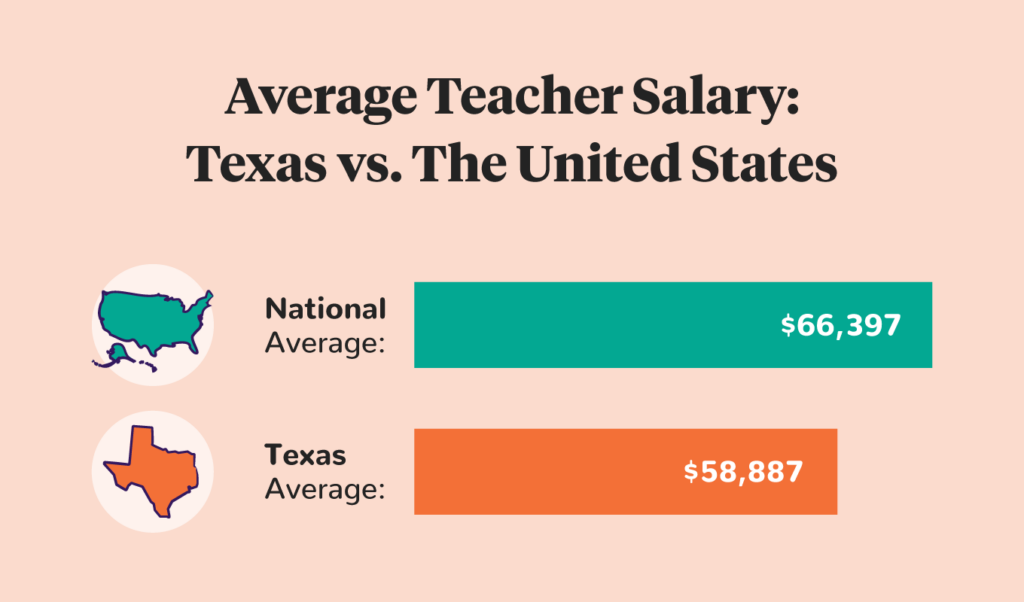
| In Texas, teachers make an average of $58,887, making it one of the best southern states for teachers’ pay. However, it ranks 26th in the entire country. |
As of 2023, public teachers in Texas make an average of $58,887, though it varies significantly throughout the state. Beyond salary, some reasons to become a teacher in Texas include job security, working within a school calendar, and plenty of job opportunities.
However, Texas teachers make 13% less than the national average of $66,397 for K-12 teachers, putting Texas in 26th place for teacher salaries. Many teachers in different states feel under-compensated — especially those who earn less than the national average, like Texas.
With just under 360,000 teachers, Texas still needs more people to become teachers in Texas. Between 2018 and 2028, demand is projected to increase by 11%, particularly in STEM subjects and special education — two of the highest-paying teacher positions. However, the low average salary has discouraged many young professionals from considering a teaching career, but new legislation in motion may change perceptions.
In this post, we’ll cover the other factors that influence how much teachers make in Texas, what types of teachers are paid the most, and how to earn additional income as a teacher.
Factors Influencing Teacher Salaries in Texas
Teacher salaries vary significantly due to numerous factors that play into how much a teacher earns. Most significantly, it comes down to:
- Experience
- Location
- School type
- Grade level
Experience Level
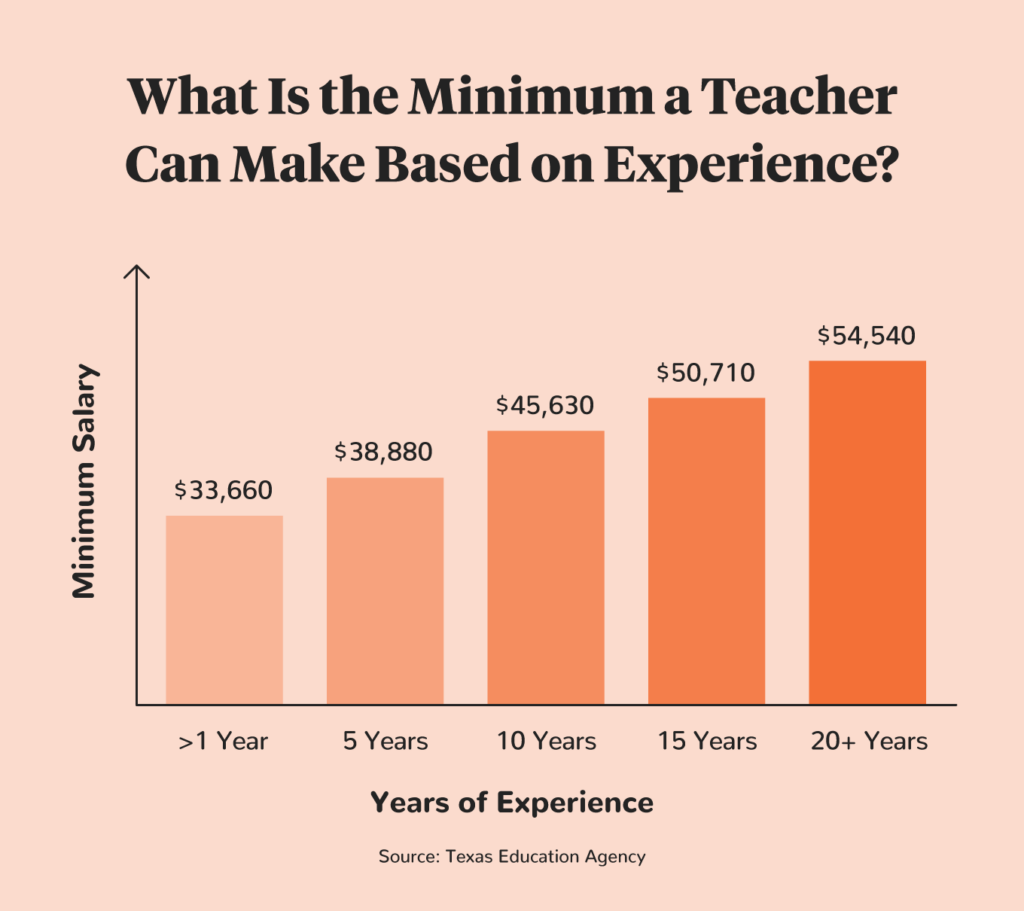
Teacher salaries in Texas depend largely on experience level. According to the Texas Education Agency (TEA), the lowest pay for an entry-level teacher anywhere in Texas is $33,660 per year. After 20 years, teachers in Texas make at least $54,540 annually.
However, this minimum salary requirement is much lower than what experienced teachers actually earn in Texas. It’s not uncommon for those with long teaching histories to make upwards of $70,000 to $80,000 per year as tenured educators.
One of the biggest perks of being a teacher is reaching tenure after about three years. Tenure ensures teachers a permanent position for the remainder of their career if they wish to remain at that school. It promises a slow but steady salary growth and protection from being fired (within reason).
Location
Physical location is one of the biggest contributing factors to a well-paying salary, regardless of profession or location. Teachers in West Texas tend to earn less. For example, an entry-level teacher in Houston earns about $43,258, whereas an entry-level teacher in Alpine earns a median salary of $36,856. This difference is partially due to discrepancies in the cost of living between the regions.
Similarly, pay varies between school districts, even within one region. For example, urban school districts pay slightly less than the suburban districts that surround them. Major suburban school districts pay the highest, while rural school districts tend to pay the least.
The difference in salaries between locations also comes down to campus type and union standings. It might seem surprising, but public schools pay more than private and charter schools. Additionally, teachers who are unionized through the Texas State Teacher Association (TSTA) often earn higher salaries than those who are not, due to the union’s collective bargaining abilities.
School Level
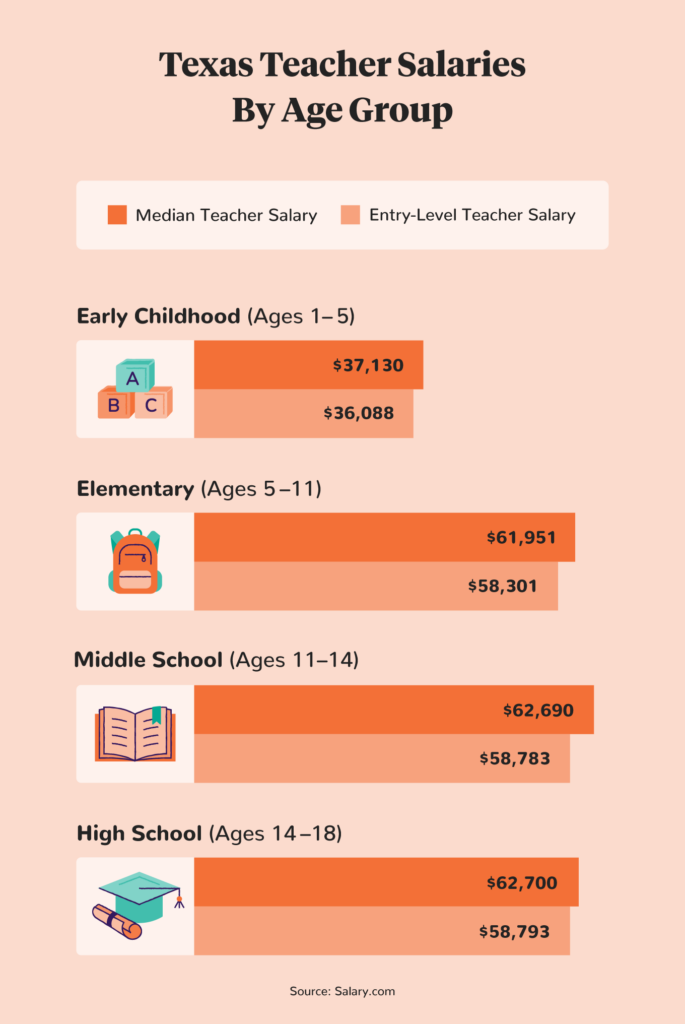
In the U.S., the age group and grade level also impact how much teachers make. High school teachers earn the highest salaries, while preschool teachers earn the lowest.
Though the difference between primary and secondary school teachers’ average salaries is minimal, it’s still apparent. The difference may be attributed to the additional subject specializations required for higher education. For example, STEM teachers tend to earn more than arts-based subjects such as foreign language or music.
Additionally, high school teachers spend more time grading assignments outside of school hours, which contributes to the slightly higher wage.
Salaries For Other Teaching Roles in Texas
Salaries for other teaching roles can vary greatly from the average salaries of primary and secondary school teachers. For example, substitute teachers make over $20,000 less than the average Texas teacher. Let’s explore four different examples of educator salaries. Keep in mind that these salaries are averages, and salaries vary within each role.
Paraprofessionals
Paraprofessionals, or teacher’s aides, assist students in subjects like math and reading. They help the primary teacher manage the classroom and prep materials but don’t lead the classroom themselves.
Average Annual Salary: $32,839
Substitute Teachers
Substitute teacher salaries vary based on the length of the assignment, district, and school type. Unlike full-time teachers, substitutes can choose to pick up jobs at their will and work part-time schedules if desired.
Average Annual Salary: $35,455
Preschool Teachers
A preschool teacher’s primary responsibility is to prepare students for kindergarten by focusing on language, social, and motor skills.
Average Annual Salary: $37,130
Special Education Teachers
Special education teachers are one of the most in-demand educator roles in the U.S., even though they make more than the average teacher. Their role is that of a typical school teacher, but they work with students who have special needs and require extra certification by passing the special education TExES exam.
Average Annual Salary: $59,576
Texas Legislation on Education
Lawmakers in Texas are actively working to improve teacher salaries. Two legislative bills were recently proposed between the Texas Senate and House of Representatives to address teacher salaries for the 2023–2024 school year.
The Senate’s bill, SB9, addresses many concerns facing teachers and schools in Texas today, including compensation. The proposed TX SB9 bill aims to reduce the pay gap between urban and rural teachers. If approved, all Texas teachers would receive at least a $2,000 raise as part of the revised Teacher Retention Allotment. Teachers in districts with fewer than 20,000 students would receive an additional $4,000, totaling $6,000. However, this would expire after 2025 and only applies to classroom teachers.
The House’s bill, House Bill 1548, presents a $15,000 raise across the board, funded by $47 billion of unused state funds. This Senate bill would increase the minimum teacher salary to $48,660 (and the average to $73,887) in Texas. It would also cover other school employees, including school nurses, librarians, and counselors.
Both bills wish to incentivize teachers and improve retention rates, which steadily fall from about 90% to 60% between teachers’ first and fifth years of teaching. While passing one of the bills can move the needle to fairly compensating Texas teachers, the state doesn’t completely govern teacher salaries.
Ways to Earn More as a Teacher in Texas
With teachers in the U.S. earning less than $20 per hour, it’s not uncommon for them to take up side projects to earn more alongside their full-time position. These roles might be available at your school or a nearby school outside of work hours.
-
- Tutor on the side: Tutoring is a great way to put your expertise to work and earn supplemental income. It’s flexible — you set your hours and tutoring fee.
- Proctor standardized tests: You can spend your weekends proctoring SAT, ACT, and advanced placement tests for high schoolers. Since this is a supervisory role, you can use that time for grading your students’ assignments.
- Pursue an advanced degree: While a bachelor’s degree in education and state licensure are requirements to be a teacher in the U.S., only a few states require teachers to spend additional years in school to obtain a master’s degree to teach. Pursuing an advanced certificate with the National Board for Professional Teaching Standards (NBPTS) can come with a pay increase and career advancement opportunities.
- Find more opportunities at your school: As a teacher, you may find opportunities to earn a side income, like chaperoning events, coaching sports, and advising student clubs.
- Sign up to teach summer school: You can teach summer courses to earn extra money during summer break. Summer school allows students to make up credits or grades, take enrichment subjects not otherwise covered in the school year, and stay caught up during the long break.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have any remaining questions on teachers’ salaries in Texas? We have answers!
How Much Does a First-Year Teacher Make in Texas?
In Texas, a first-year teacher earns a median salary of about $41,902 per year. This amount includes teachers at all grade levels, subjects, and locations within the state. You could earn much more depending on your area of expertise and school.
Do Texas Teachers Get Paid Over the Summer?
Texas teachers get paid for the hours and months they work throughout the year, meaning they typically do not get paid over the summer. However, some institutions allow teachers to evenly spread their salary payout throughout the year.
Do Teachers Get Paid For Overtime in Texas?
In Texas, teachers typically don’t qualify for paid overtime. State law mandates that employees who work over 40 hours a week receive overtime pay, but it doesn’t apply to executive, administrative, or salaried positions.
Time spent on grading, lesson planning, or other preparation activities outside school hours does not count toward overtime. This is because most teachers have “free periods” where they are expected to complete those tasks. However, many teachers ultimately use their own time for these tasks.
Do Texas Teachers Get Paid Well?
Most people can agree that teachers across the country are not paid as well as they should be, and Texas is no exception. Compared to the U.S., Texas ranks right in the middle at 26th. However, Texas is among the best Southern states for teachers’ pay. Teachers in Texas can expect to see salaries similar to teachers in Maine, Colorado, and Iowa.
Both the Texas Senate and House of Representatives are working toward ensuring teachers are fairly compensated with their respective bills.
The demand for teachers in Texas is high. If you’re considering a teaching career, an alternate certification might be right for you. Check out our list of the best alternative certification programs in Texas to get started.
Already in the process of becoming a teacher in Texas? Use our study guides to ace your TExEs exam.